There are three main measurings of the cutting effect for diamond saw blade: efficiency, lifespan, and processing quality.
The cutting efficiency reflects the sharpness and production efficiency; the cutting life reflects the durability of the saw blade and is often expressed by the number of cutting materials (cubic, squared, linear meters, number of blocks, etc.). Cutting life is not as long as possible, it is necessary to consider with the cutting efficiency, to achieve a good economy is the most appropriate; processing quality refers to the flatness of the sawing surface, flatness, parallelism on both sides and edge integrity .
There are many factors influencing the cutting effect of diamond circular saw blades,there are two aspects the manufacturing and use factors. Manufacturing factors include raw materials, manufacturing processes (diamonds, binders, core blanks and formulars, hot pressing, welding, shaping), etc.; use factors refer to the choice of saw blade, the saw machinery, the selection of sawing parameters, and the installation of the saw blade. , operation, etc.
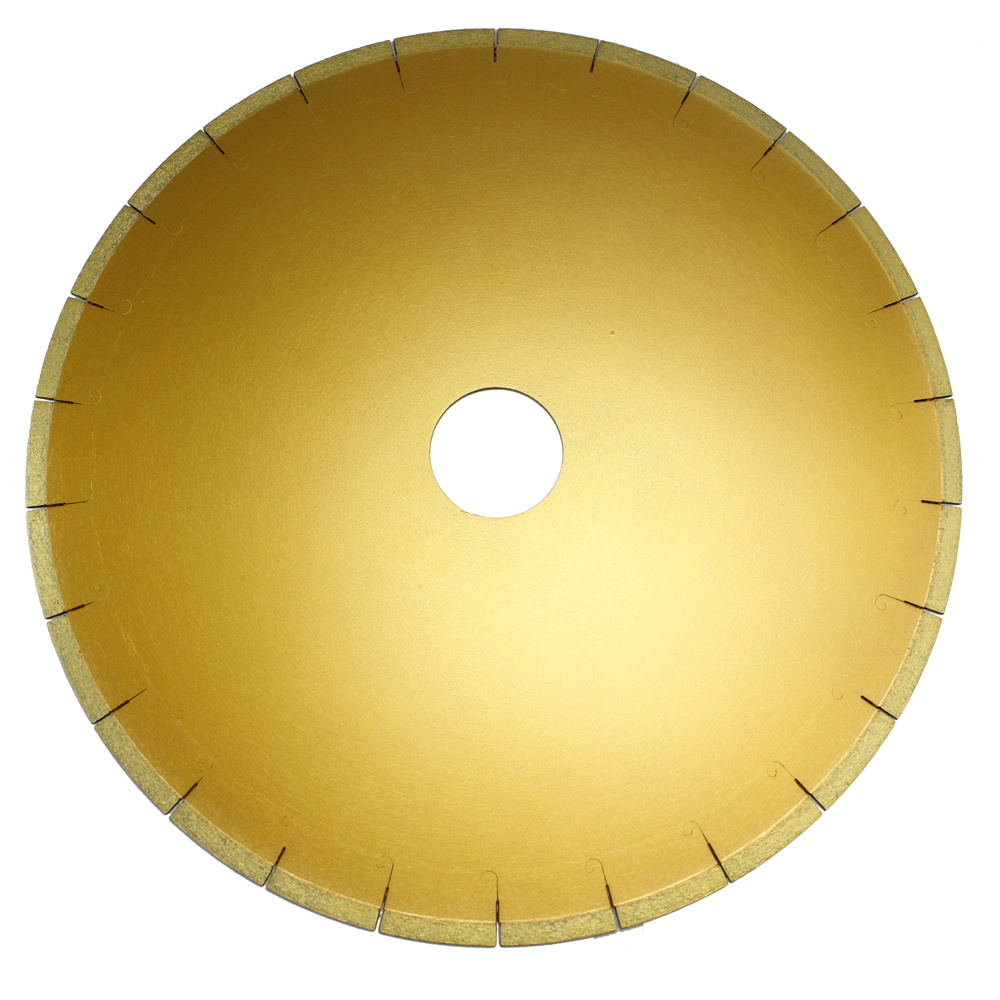
1. the struture and size selection of saw blade:
The salesman is required to be familiar with the conventional structure, size, and maximum cutting depth (which can be 1/3 of the diameter of the saw blade) of the circular saw blade of diameter ¢105-2200mm, and should be able to recommend a reasonable structure and size according to the processing conditions.
(1) The Selection of core material:
The core must have sufficient strength, rigidity and hardness. Genarally, the hardness of core requires HRC 35-42, the maximum surface roughness is Ra 3.2um; the surface may not have cracks, burrs, or rust; the core must be eliminate distrorted forces, micro-cracks, to ensure tensile stress balance, flatness and other shape requirments and appearance, internal quality requirements.
At present , hot-pressed, high-frequency welding core material used high quality spring steel 65Mn, 50Mn2V, laser welding saw blade core use tempered steel 30CrMo, 35CrMo, because of its low carbon content, laser welding and the transition layer solder well.
Core structure selection:
From the structure, as usual the core can be divided into continuous type and a water outlet type.
The continuous core is mainly used for the production of hot-pressed saw blades, its edges are mostly of thin walled teeth, the water-outlet type core can be used for welding or hot pressing.
The core of Narrow water slot (small U, Key slot) is for cutting weakly abrasive or brittle materials (such as limestone, marble, microlite stone, glazed tiles or granite) medium diameter saw blade, wide water slot core (large U-slot) is used for large size blade or medium-size that cut strong abraive materials (such as sandstone, concrete, asphalt pavement, wall, refractories, etc),which facilitates large amounts of coolant flowing into the cuts for chipping and cooling.
Table 1 Dimension of saw blade Unit: mm
| Outside diameter of blade | Outside diameter of core | The thickness of core | Bore size | Number of slot (Width or Narrow | Dimension of segment | ||
| Length | Height | Width | |||||
| 105 | 91 | 1.2/1.4 | 22.23 | -/8 | 32~35 | 8、10、12 | 1.8/2/2.2 |
| 115 | 101 | -/9 | |||||
| 125 | 111 | -/10 | 2/2.2/2.4 | ||||
| 150 | 136 | 1.4/1.6/1.8 | -/12 | ||||
| 180 | 166 | -/14 | |||||
| 200 | 191 | 1.6/1.8/2 | -/16 | 2.4/2.8 | |||
| 230 | 216 | -/18 | |||||
| 250 | 236/240 | 1.8/2 /2.2 | 25.4/50/60 | -/17 | 40,42,45, Fan-shape, Slanted shape | 8、10、12、15、20 | 2.6/2.8/3 |
| 300 | 286/290 | -/21 | |||||
| 350 | 336/340 | 2/2.2/2.4 | 21/24、25 | 2.8/3/3.2/3 | |||
On the narrow nozzle steel , segment can be close to each other, which will improve the continuity of sawing, mitigate the impact, and reduce chipping, thus extending the lifespan of saw blade. Nevertheless, the stress at the bottom of the nozzle is more concentrated in this case, formulating cracks. As a result, the stone may be uneven, especially for dry cutting.
Overall, granite cutting blades are largely used on the small U-shape and keyhole steel; marble cutting blades on the very narrow U-shape steel; reinforced concrete blades on the keyhole steel; green concrete blades and asphalt blades on the large U-shape steel with protected teeth.
It is worthy of mark that the opening of the steel can prolong its outer edge to some extent, and increase the stress. This design can compensate for edge extension caused by thermal or centrifugal force during welding and use, which redounds to non-deforming production (integral hot pressing, welding compensation thermal stress, or shrinkage stress of the steel), chip removal and cooling in usage, as well as the reduction of swing and ‘S’ cutting path. However, the steel with an opening is vulnerable to cracks and abrasive wear during use, which is mainly attributed to the fact that the force is repeatedly concentrated on the bottom of the nozzle in cutting (stretching and compressing), resulting in fatigue cracks. Generally, enlarging the radius of the arc at the bottom of the nozzle is conducive to dispersing the stress. Thus, once a crack is found, it is feasible to drill a round hole at the root of the crack, preventing the further spread of the crack. In addition, the saw blade with protected teeth can be used to reduce the wear of the girdle on the opening of the nozzle matrix in cutting strong abrasive stone.
The silent steel can lower the noise produced by saw blades in cutting. Such steel is mostly composed of composite materials: adding a layer of materials (copper foil, rubber, elastic polymer) with the high sound absorption coefficient into the middle of the steel ; filling the spoon-shape nozzle in the steel with a better sound-absorbing copper sheet; regularly cutting some ‘S’- and ‘C’-shape seams with laser along the bottom and center hole of the nozzle at the radial direction, and then pouring special resin materials into these seams.
2. Diamond selection
As a kind of rough working, diamond saw blade cutting has a high requirement for efficiency and lifespan. The diamond should have reasonable wear and fragment shedding, while giving full play to its role. Both the premature consumption and excessive wear resistance of diamond are adverse to the cutting process. The former means that the diamond fails to function properly, which may be caused by a variety of factors: the steel is not wear-resistant or is weak to control the diamond; the cutting spend or the feeding speed is too high; the abrasive property of the stone is too strong; or the diamond has poor quality and low concentration if large fragments are found. The premature consumption of diamond is usually featured by low cutting efficiency and short lifespan. Therefore, in addition to adjusting the diamond and the anchoring agent, it is necessary to increase cutting speed, enlarge cutting depth and decrease feeding for reducing the crush and shedding of the diamond, as well as the wear of the anchoring agent. This method can enhance cutting efficiency and prolong the lifespan. By contrast, when the diamond has excessive wear resistance, the stone will be ground into a flat or smooth arc surface, and it is hard to produce micro crushing, which means that the anchoring agent matrix is over wear-resistant or it has too much control of the diamond; the cutting depth of the saw blade is large; the feeding is small; the processed material is hard and fine; the diamond has good quality and high concentration; the cutting depth of diamond particles into the rock is small; diamond particles are subjected to low impact and cutting force. In this case, the saw blade will have low cutting efficiency and long life macroscopically. Therefore, both the diamond and the anchoring agent should be modified. Meanwhile, it is essential to slow cutting speed, narrow cutting depth, and increase feeding, which can motivate the diamond to produce micro fractures and accelerate matrix wear, thus improve cutting efficiency.
Usually, the crush & impact resistance of good quality diamond is better, wearing out slowly and little broken when cutting, so it is very suitable used for cutting strong abrasiveness material like:sandstone, concrete pavement, bituminous pavement, refractory material. In the mean time, Diamond should easy plating,Coarse grit, low Concentration, the bond bond should be high abrasiveness with strong holding force for diamond; the lower grade diamond, cuz the rush & impact resistance is relatively worse,is suitable for cutting easy-cutting material, and the grit should be fine, concentration should be higher, bond should be softer.
There is One thing should be pay special attention: for high temperature & wear-resisting bond, high grade diamond and hard cutting material, if you mix some low grade diamond, would decrease obviously the cutting efficiency and life.
Diamond grit 30/35-60/70 is mostly used in blade. When cutting high abrasive material the grit should be coarse, cutting very hard,high density Granite and crisp glass, the grit should be fine.
Increasing concentration of diamond can longer the blade life by reducing cutting force of each diamond which reduce the wearance.But on the other hand,it reduce also the cutting efficiency and increase the cost. Theoretically, there would exist a most economic concentration.
According to different cutting requirements, the concentration of blade would range 10/50%. Small blade mostly range between 10-20%, medium diameter blade 15-40%, big size blade 25-50%.
Tips: diamond concentration means how many diamond included in segment layers.
Stipulating: diamond volume takes up 25% of diamond layer (equal to including 4.4ct/cm3 diamond), the concentration is 100%,And so on.
3.Bond Selection
Usualy, cutting soft or low abrasive/ no abrasive material like glass, glazed ceramic tiles, soft marble, the bond should be soft, not wear resistance and some brittleness bond like bronzed bond, cobalt bronze bond or Iron bronze bond.
Diamond should have sharp angularity, rough surface. Cutting speed,depth, feeding, can be bigger, but should pay attention to the brittleness of cutting material can bear or not to avoid chipping.
Cutting medium abrasive or medium hardness material like Ordinary marble,limestone, bluestone,soft granite(balsalt) and cutting hard and high density granite, it is suitable choose bronzed bond, cobalt bronze bond or Iron bronze bond, The bond should has higher abrasiveness , plastically and holing force for Diamond. The diamond surface should be rough, suitable for plating. The cutting parameter decided by hardness of cutting material. The high hardness would easy force to impactive cutting, so the cutting speed and cutting depth should not be too fast and too deep. But the feeding speed should be fast. When the hardness is not very high, the cutting speed should be fast, cutting depth should bigger.
For high abrasive material like coarse quartz granite, sandstone, concrete and refractory brick …etc, requested the blade bond should be high abrasiveness, high hardness, lower plastically, higher diamond holding force, iron bond and WC bond is suitable. And it is suitable choose high quality diamond, good heat resistance, easy plating. Cutting high hardness and strong abrasiveness material, would force to impactive cutting ,so the cutting speed and cutting depth should not be too fast and too deep. But the feeding speed should be fast. To the contrary, cutting lower hardness and strong abrasiveness material, cutting speed should be fast, big cutting depth and slow feeding speed., in thisway would validly keep the cutting efficiency and reduce the wearing of the bond and diamond, avoid diamond falling out.
For dry cutting blade, it is suitable choose non-softenable bond with good thermal conductance, strong holding force for diamond, so the cobalt bond is more suitable, also the tungsten bond. The head resistance of diamond should be good, and suitable for plating. And the design of diamond segment & steel core shape which should easy for chip removing and increasing cooling result.
4. “Match cutting” principle
Gennerally, blade choosing should obey” Match cutting “ principle, which means all parameter of blade (like diamond quality grade, grit, concentration, bond performance, segment shape & size, core shape & size, welding …etc) should correspondingly matched with cutting material property , cutting machine property,and cutting parameter which could make the best cutting result. Once there has matching mistake, would result to un-cutting or low life.
There is some brief introduction different application of different blade as below:
(1)General purpose blade( including hot press blade and laser welding blade)
Suitable cutting: Stone,wall/floor tiles, concrete with steel, asphalt. Turbo segment also suitable for old concrete, hard brick, suitable for dry cutting or intermittent dry cutting. Long time cutting concrete with steel and asphalt, the life is not enough.
Un-suitable cutting: strong abrasiveness material like sandstone and heave refractory bricks, though it is ok for cutting but short life.
This kind of blade cannot cut glass, fine ceramic..etc.
Manufacturing basis: Mainly can well cutting stone, and wall/floor tiles
(2)Professional Blade(Like granite blade, marble blade, sandstone blade, fresh-concrete blade, steel concrete blade, asphalt blade and wall saw) was design to fix cutting material, but also suitable for cutting others.